Hiding Behind A Mask Drawing
- Adobe Premiere Pro User Guide
- Beta releases
- Beta Program Overview
- Premiere Pro Beta Home
- Features in Beta
- New import & export in Premiere Pro (Beta)
- FAQ | New import and export in Premiere Pro (Beta)
- Getting started
- Get started with Adobe Premiere Pro
- What's new in Premiere Pro
- Release Notes | Premiere Pro
- Keyboard shortcuts in Premiere Pro
- Accessibility in Premiere Pro
- Get started with Adobe Premiere Pro
- Hardware and operating system requirements
- Hardware recommendations
- System requirements
- GPU and GPU Driver requirements
- GPU Accelerated Rendering & Hardware Encoding/Decoding
- Hardware recommendations
- Creating projects
- Creating projects
- Open projects
- Move and delete projects
- Work with multiple open projects
- Work with Project Shortcuts
- Backward compatibility of Premiere Pro projects
- Open and edit Premiere Rush projects in Premiere Pro
- Best Practices: Create your own project templates
- Workspaces and workflows
- Workspaces
- Working with Panels
- Windows touch and gesture controls
- Workspaces
- Capturing and importing
- Capturing
- Capturing and digitizing footage
- Capturing HD, DV, or HDV video
- Batch capturing and recapturing
- Setting up your system for HD, DV, or HDV capture
- Capturing and digitizing footage
- Importing
- Transferring and importing files
- Importing still images
- Importing digital audio
- Transferring and importing files
- Importing from Avid or Final Cut
- Importing AAF project files from Avid Media Composer
- Importing XML project files from Final Cut Pro 7 and Final Cut Pro X
- Importing AAF project files from Avid Media Composer
- Supported file formats
- Digitizing analog video
- Working with timecode
- Capturing
- Editing
- Sequences
- Create and change sequences
- Add clips to sequences
- Rearrange clips in a sequence
- Find, select, and group clips in a sequence
- Edit from sequences loaded into the Source Monitor
- Simplify sequences
- Rendering and previewing sequences
- Working with markers
- Scene edit detection
- Video
- Create and play clips
- Trimming clips
- Synchronizing audio and video with Merge Clips
- Render and replace media
- Undo, history, and events
- Freeze and hold frames
- Working with aspect ratios
- Create and play clips
- Audio
- Overview of audio in Premiere Pro
- Audio Track Mixer
- Adjusting volume levels
- Editing, repairing and improving audio using Essential Sound panel
- Monitor clip volume and pan using Audio Clip Mixer
- Audio balancing and panning
- Advanced Audio - Submixes, downmixing, and routing
- Audio effects and transitions
- Working with audio transitions
- Apply effects to audio
- Measure audio using the Loudness Radar effect
- Recording audio mixes
- Editing audio in the timeline
- Audio channel mapping in Premiere Pro
- Use Adobe Stock audio in Premiere Pro
- Overview of audio in Premiere Pro
- Advanced editing
- Multi-camera editing workflow
- Editing workflows for feature films
- Set up and use Head Mounted Display for immersive video in Premiere Pro
- Editing VR
- Multi-camera editing workflow
- Best Practices
- Best Practices: Mix audio faster
- Best Practices: Editing efficiently
- Best Practices: Mix audio faster
- Sequences
- Video Effects and Transitions
- Overview of video effects and transitions
- Effects
- Types of effects in Premiere Pro
- Apply and remove effects
- Effect presets
- Automatically reframe video for different social media channels
- Color correction effects
- Change duration and speed of clips
- Adjustment Layers
- Stabilize footage
- Transitions
- Applying transitions in Premiere Pro
- Modifying and customizing transitions
- Morph Cut
- Graphics, Titles, and Animation
- Graphics and titles
- Create titles and motion graphics
- Applying text gradients in Premiere Pro
- Using Motion Graphics templates for titles
- Replace images or videos in Motion Graphics templates
- Use data-driven Motion Graphics templates
- Best Practices: Faster graphics workflows
- Add Responsive Design features to your graphics
- Working with captions
- Speech to Text
- Speech to Text in Premiere Pro | FAQ
- Upgrade Legacy titles to Source Graphics
- Create titles and motion graphics
- Animation and Keyframing
- Adding, navigating, and setting keyframes
- Animating effects
- Use Motion effect to edit and animate clips
- Optimize keyframe automation
- Moving and copying keyframes
- Viewing and adjusting effects and keyframes
- Adding, navigating, and setting keyframes
- Graphics and titles
- Compositing
- Compositing, alpha channels, and adjusting clip opacity
- Masking and tracking
- Blending modes
- Compositing, alpha channels, and adjusting clip opacity
- Color Correction and Grading
- Overview: Color workflows in Premiere Pro
- Get creative with color using Lumetri looks
- Adjust color using RBG and Hue Saturation Curves
- Correct and match colors between shots
- Using HSL Secondary controls in the Lumetri Color panel
- Create vignettes
- Looks and LUTs
- Lumetri scopes
- Display Color Management
- HDR for broadcasters
- Enable DirectX HDR support
- Exporting media
- Workflow and overview for exporting
- Quick export
- Exporting for the Web and mobile devices
- Export a still image
- Exporting projects for other applications
- Exporting OMF files for Pro Tools
- Export to Panasonic P2 format
- Exporting to DVD or Blu-ray Disc
- Best Practices: Export faster
- Workflow and overview for exporting
- Working with other Adobe applications
- After Effects and Photoshop
- Dynamic Link
- Audition
- Prelude
- Organizing and Managing Assets
- Working in the Project panel
- Organize assets in the Project panel
- Playing assets
- Search assets
- Creative Cloud Libraries
- Sync Settings in Premiere Pro
- Using Productions
- How clips work across projects in a Production
- Consolidate, transcode, and archive projects
- Managing metadata
- Best Practices
- Best Practices: Working with Productions
- Best Practices: Learning from broadcast production
- Best Practices: Working with native formats
- Best Practices: Working with Productions
- Working in the Project panel
- Improving Performance and Troubleshooting
- Set preferences
- Reset preferences
- Working with Proxies
- Proxy overview
- Ingest and Proxy Workflow
- Proxy overview
- Check if your system is compatible with Premiere Pro
- Premiere Pro for Apple silicon
- Eliminate flicker
- Interlacing and field order
- Smart rendering
- Control surface support
- Best Practices: Working with native formats
- Knowledge Base
- Green and pink video in Premiere Pro or Premiere Rush
- How do I manage the Media Cache in Premiere Pro?
- Fix errors when rendering or exporting
- Troubleshoot issues related to playback and performance in Premiere Pro
- Green and pink video in Premiere Pro or Premiere Rush
- Monitoring Assets and Offline Media
- Monitoring assets
- Using the Source Monitor and Program Monitor
- Using the Reference Monitor
- Offline media
- Working with offline clips
- Creating clips for offline editing
- Relinking offline media
- Working with offline clips
- Monitoring assets
Use Premiere Pro's masking tools to apply effects to a specific part of a frame in your video. Learn to apply a mask, and then track it as it moves across the frame.
Masking in Premiere Pro
Masks let you define a specific area in a clip that you want to blur, cover, highlight, apply effects, or color-correct. You can create and modify different shaped masks, like an Ellipse or a Rectangle. Or, you can draw free-form Bezier shapes using the Pen tool.
Create masks using shapes
You can use the Ellipse shape tool to create a circular or ellipse-shaped mask, or a Rectangle shape tool to create a four-sided polygon.


-
In the Timeline panel, select the clip you want to mask.
-
From the Effects panel, select the effect that you want to apply to the clip.
For example, if you want to apply the Mosaic effect, select Video Effects > Stylize > Mosaic.
-
Apply the selected effect to a clip by dragging the effect from the Effects panel to the clip in the Timeline panel. Alternatively, select the clip and double-click an effect in the Effects panel to apply it.
For more information on applying an effect, see Apply effects to clips.

Add mosaic effect to a clip -

Ellipse, rectangle, pen tool Open the Effect Controls panel to see the effect properties. Click the drop-down arrow to reveal the controls.
You can create an ellipse or rectangle. Use the Pen tool to create free form shapes.
You can specify values to adjust a mask using theEffect Controls panel. The controls change depending on your choice. For more information, see Adjust mask settings.
-
Click the Ellipse shape tool to create an Ellipse-shaped mask or click the Rectangle shape tool to create a rectangle-shaped mask.
The shape mask appears in the clip displayed in the Program Monitor, and the effect is constrained within the masked area.

Ellipse -
You can now customize the size and shape of the mask using the Effect Controls panel. For more information on editing your mask, see Adjust mask settings.

Create a mask using the Ellipse tool
You can apply the same effect multiple times by using different settings each time.
![]() Important notes
Important notes
- Premiere Pro does not save masks as effects presets.
- Masking is disabled for the Warp Stabilizer effect. The mask shape controls do not appear for the Warp Stabilizer effect in the Effect Controls Panel.
Create free-form shapes
You can create free-form shapes using the Pen tool. The Pen Tool lets you freely draw complex mask shapes around objects.
Select the Pen tool from the Effect Controls panel. Draw directly on the clip in the Program Monitor.
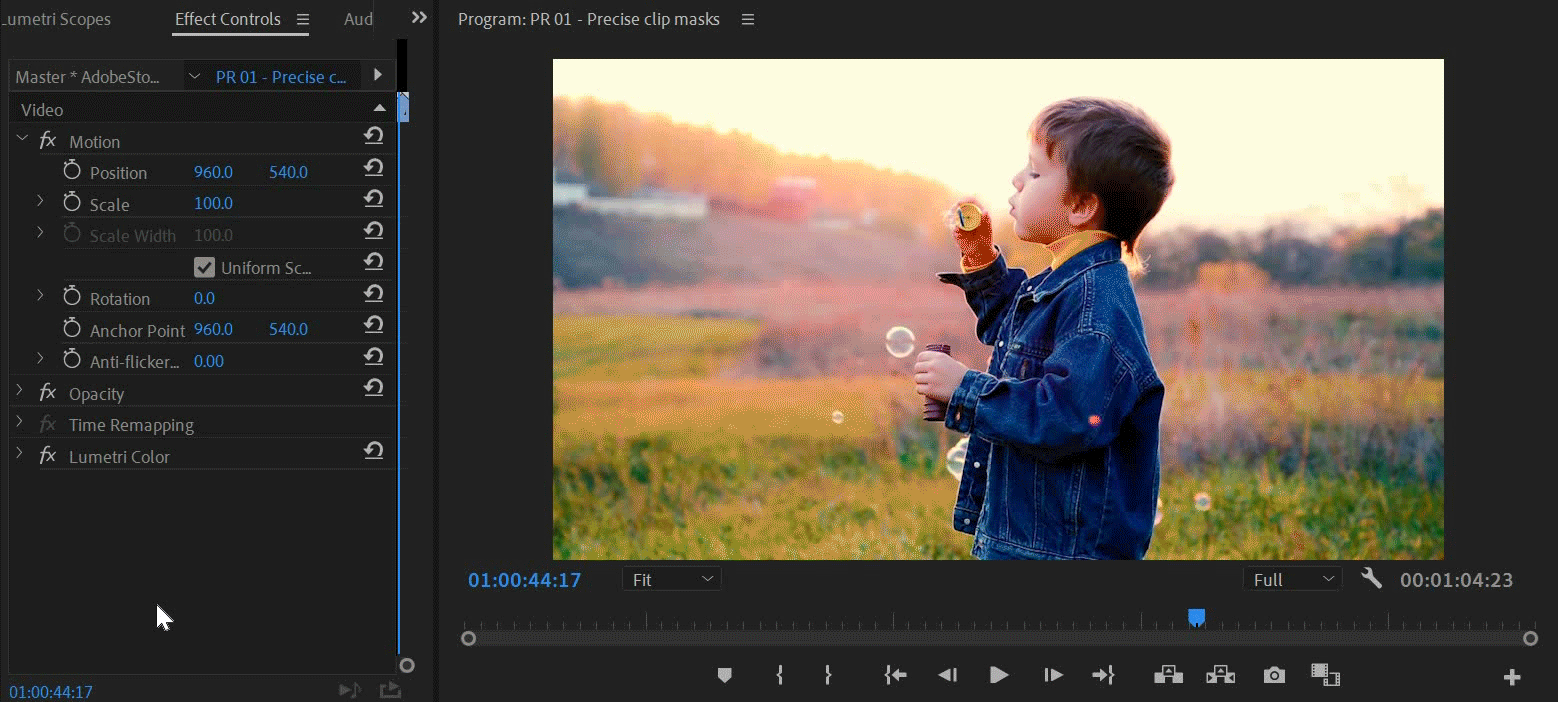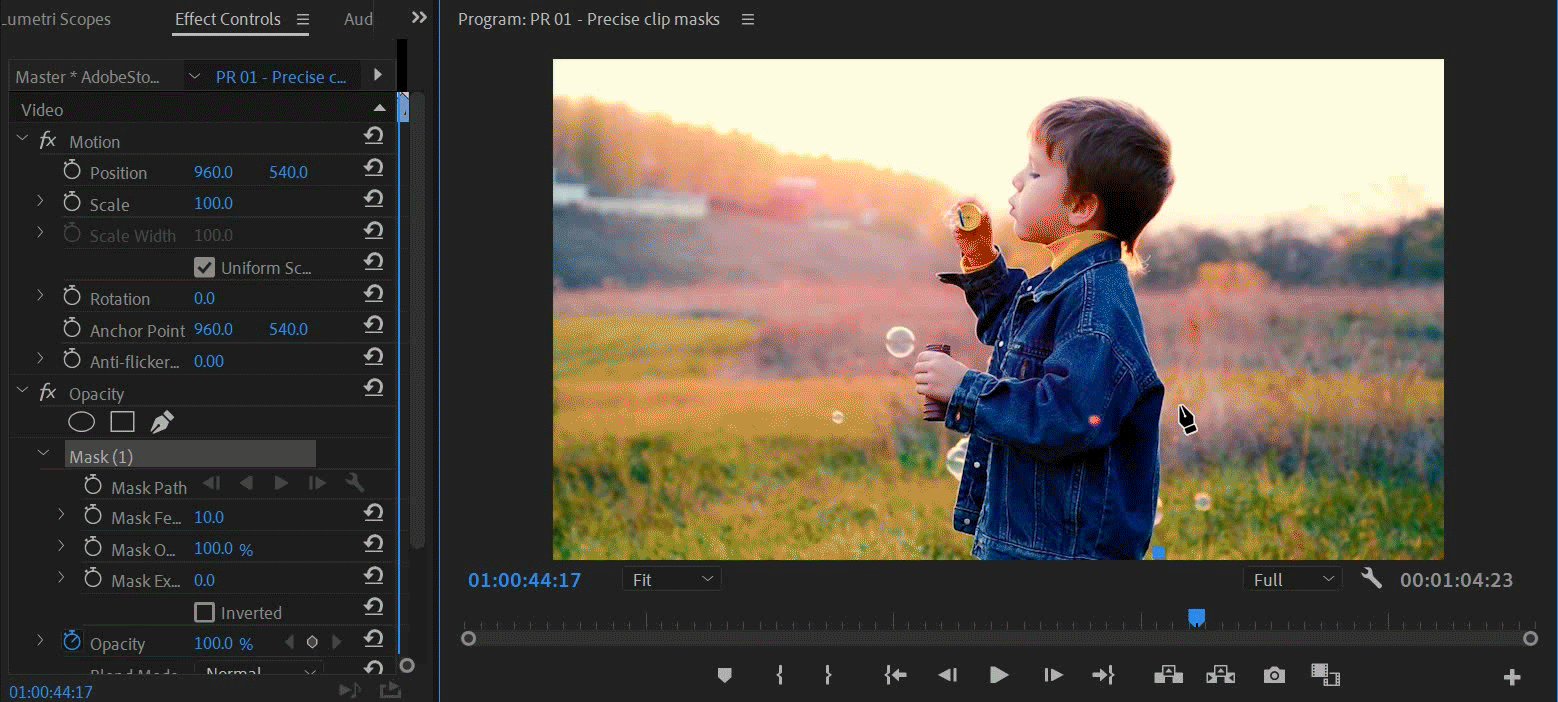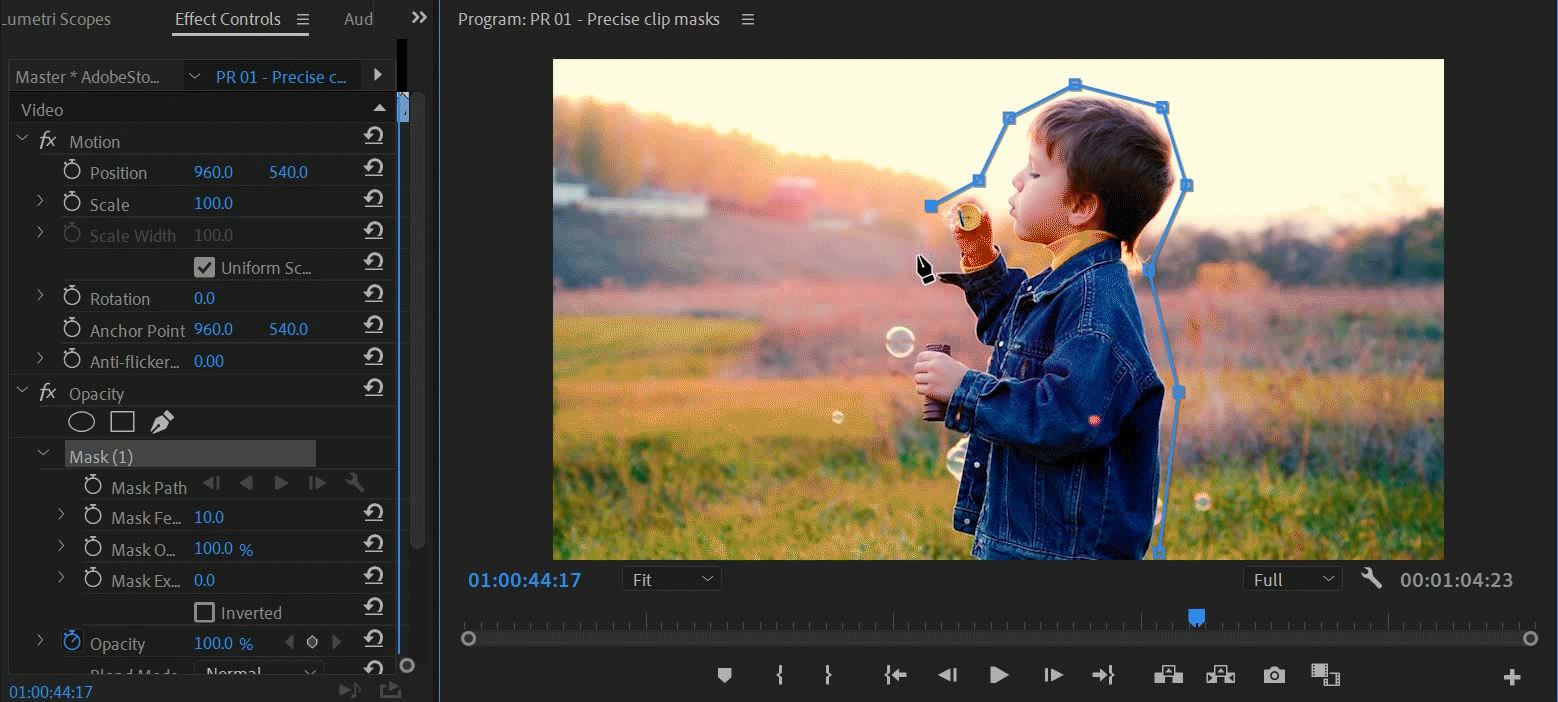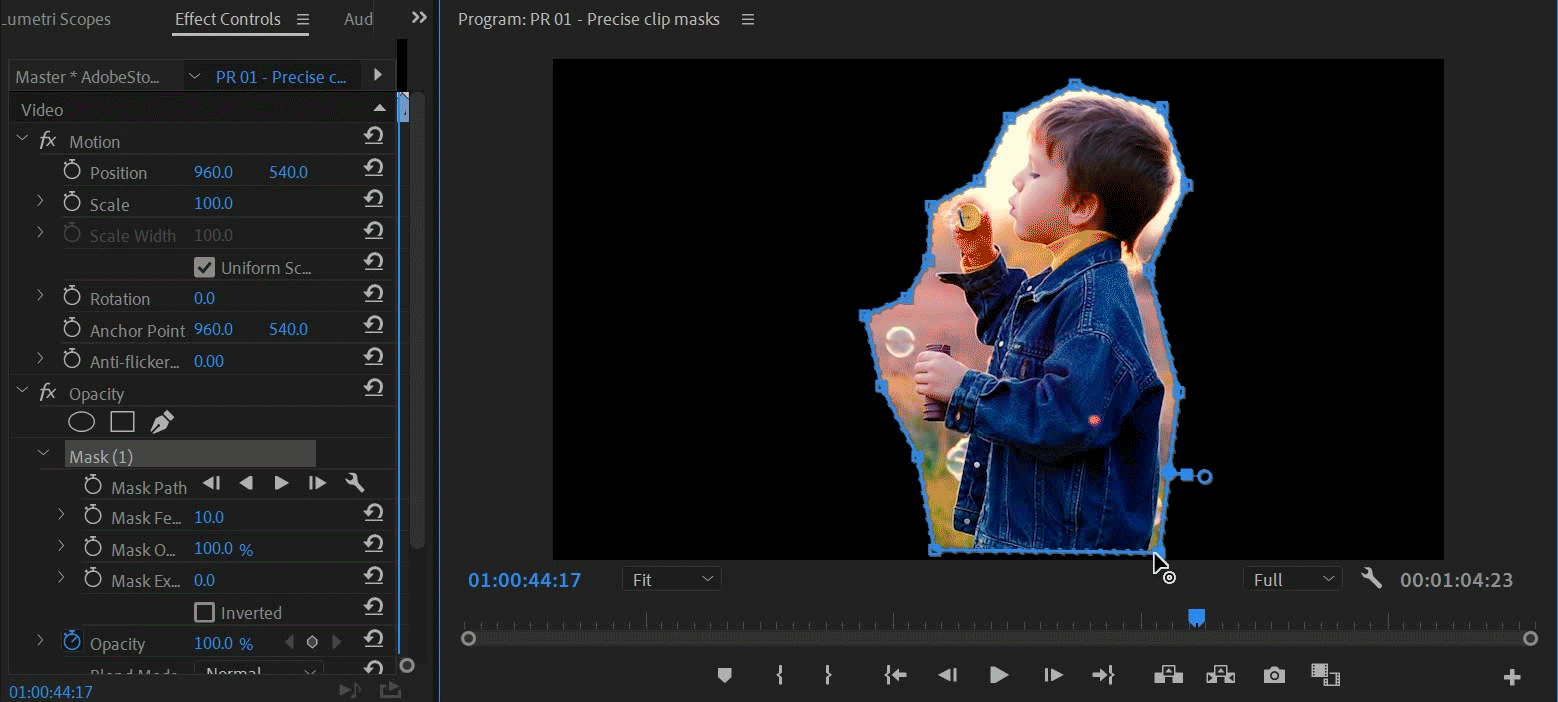
You can create different shapes by drawing straight lines and curved segments. To draw smooth curves, you can draw Bezier path segments that provide you greater control over the shape of the mask.
The simplest path that you can draw with the Pen tool is a straight line with two vertex points. By continuing to click, you create a path made of straight-line segments connected by vertex points. This is a linear mask.
A linear mask is always a polygon with joined by hard angles. Linear control points are also known as corner points.

-
Position the Pen tool where you want the straight segment to begin, and click to define the first vertex point (do not drag).
The first segment you draw is not visible until you click a second vertex point.
-
Click again where you want the segment to end (Shift-click to constrain the angle of the segment to a multiple of 45°).
-
Continue clicking to set vertex points for additional straight segments.
-
To close the path with a linear mask, Alt+click (Windows) or Option+click (macOS) over the first vertex point.
You create a curved path segment by dragging direction lines using the Pen tool. The length and direction of the direction lines determine the shape of the curve.
To create Bezier shapes, you convert a vertex point on a mask to a Bezier point by pressing the Alt key while placing the cursor over the vertex point. The cursor becomes an inverted "V" shape ![]() . Then, click and release the pointer.
. Then, click and release the pointer.
Bezier handles provide two-directional controls that allow you to change the curve of the line segment between the handle and the next point on either side.
![]()
A. Two-directional Bezier handles to control the shape of the curveB. Bezier mask points
-
Place the Pen tool where you want the curve to begin, and hold the mouse button down. A vertex appears, and the Pen tool pointer changes to an arrowhead.
-
Drag to modify the length and direction of both direction lines for a vertex, and then release the mouse button.
A. Placing the Pen tool
B. Starting to drag (mouse button pressed)
C. Dragging to extend direction lines
Drawing the first vertex in a curved path -
Place the Pen tool where you want the curved segment to end, and do one of the following:
- To create a C-shaped curve, drag in the direction opposite from the direction that you dragged the previous direction line, and then release the mouse button.
A. Starting to drag
B. Dragging away from previous direction line, creating a C curve
C. Result after releasing mouse button
Drawing the second vertex in a curved path - To create an S-shaped curve, drag in the same direction as the previous direction line, and then release the mouse button.
A. Starting to drag
B. Dragging in same direction as previous direction line, creating an S curve
C. Result after releasing mouse button
Drawing an S curve -
Continue dragging the Pen tool from different locations to create a series of smooth curves.
Modifying and moving masks
The vertex points on a mask let you easily manage the shape, size, and rotation of a mask.
Modify the shape, size, and rotation of a mask
![]()
To change the shape of a mask, drag a mask handle.
![]()
To change the shape of an ellipse mask to a polygon, press Alt and click any of the vertices of the ellipse.
![]()
To resize a mask, place your cursor just outside a vertex and press Shift (cursor becomes a double-sided arrow![]() ), then drag the cursor.
), then drag the cursor.
![]()
To rotate the mask, place your cursor just outside a vertex (cursor becomes a curved double-sided arrow![]() ), and then drag.
), and then drag.
Move, add, or remove a vertex
![]()
To move a vertex, drag the vertex with the Selection tool. Note that while dragging an ellipse-shaped mask, the ellipse shape is not maintained.
![]()
To add a vertex, place your cursor over a mask edge while pressing Ctrl (Windows) or Cmd (macOS). The cursor changes to a pen shape with a "+" sign![]() .
.
![]()
To remove a vertex, place your cursor over the point while pressing Ctrl (Windows) or Cmd (macOS). The cursor changes to a pen shape with a minus sign![]() .
.
Other important commands and keyboard shortcuts
- Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to nudge a selected control point by a distance of one unit.
- Press Shift and use the arrow keys to nudge a selected control point by a distance of five units.
- To deselect all the selected control points, click outside a currently active mask.
- To disable direct manipulation of a mask, click outside the mask. Or deselect the clip in the sequence.
- To delete a mask, select the mask in the Effect Controls Panel and press Delete on your keyboard.
Adjust mask settings
You can specify values to adjust a mask using the Effect Controls panel. You can feather the mask, expand the mask, change the opacity, or invert the mask to stylise your video.

Apply mask feathering
![]()
To feather a mask, specify aMask Feather value. The feathering guide appears around the mask as a dashed line. Drag the handle away from the feathering guide to increase the feathering, or toward the feathering guide to decrease the feathering.
The mask feather handle lets you control the amount of feathering directly on the mask outline in the Program Monitor.
Adjust mask opacity
![]()
When opacity is applied to a mask it will change the opacity of the footage you have cropped out.
To adjust the opacity of a mask, specify a Mask Opacity value. The slider controls the mask opacity. At a value of 100, the mask is opaque and blocks out any underlying area of the layer. As you lower the opacity, more of the area under the mask becomes visible.
Adjust mask expansion
![]()
To expand a mask, specify aMask Expansion value. Positive values move the borders outward, and negative values move it inward. You can also drag the handle away from the expansion guide to expand the mask area, or toward the expansion guide to contract the mask area.
Invert mask selection
![]()
Select the Inverted check box to reverse the masked and unmasked areas.
You can protect areas that you want to leave as-is by masking it, and select the Inverted check box to apply effects to the unmasked areas.
Copy and paste masks
You can easily copy and paste masks between clips or between effects.
Copy and paste effects with masks between clips
When you copy and paste an effect containing masks, the pasted effect has the same masks applied.
- In the Timeline panel, select the clip containing the effect with masks.
- In the Effect Controls panel, select the effect to copy.
- Select Edit > Copy. Or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+C (Windows) or Cmd+C (Mac OS).
- Select another clip in the Timeline to which you want to paste the mask.
- Select Edit > Paste. Or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+V (Windows) or Cmd+V (Mac OS).
Copy and paste masks between effects
- In the Effect Controls panel, click the triangle to expand the effect to reveal the applied masks.
- Select the mask to copy.
- Select Edit > Copy. Or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+C (Windows) or Cmd+C (Mac OS).
- Select another effect in the Effect Controls panel to which you want to paste the mask.
- Choose Edit > Paste. Or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+V (Windows) or Cmd+V (Mac OS).
You can copy and paste only one mask at a time.
Mask tracking in Premiere Pro
When you apply a mask to an object, Premiere Pro can let the mask automatically follow the object as it moves from one frame to another. For example, after blurring a face using a shape mask, Premiere Pro can automatically track the movements of the masked face from frame to frame as the person moves.
When a mask is selected, the Effect Controls panel displays controls for tracking the mask forward or backward. You can choose to track the mask either one frame at a time or until the end of the sequence.
Click the wrench icon![]() to modify how masks are tracked. You can select from a few choices to provide the most effective tracking:
to modify how masks are tracked. You can select from a few choices to provide the most effective tracking:
Position
Tracks just the mask position from frame to frame
Position And Rotation
Tracks the mask position while changing the rotation as required per frame
Position, Scale, And Rotation
Tracks the mask position while automatically scaling and rotating as the frame moves
You can find the option that works best for your clip by trial. Select one of these options, and if it doesn't work well, undo, and try another one.
To use the more advanced tracking features available in After Effects, send your sequence to After Effects using the Dynamic Link feature. For more information, see Mask Tracking in After Effects.
Speed up mask tracking
Mask tracking in Premiere Pro is faster when Live Preview is disabled (the default option). If for some reason, Live Preview is enabled, you can disable it using the following procedure.
-
In the Timeline panel, select the clip containing the effect with masks.
-
To preview the changes in the track, click the mask wrench icon
 and select preview from the drop-down list.
and select preview from the drop-down list.
Mask preview -
To disable live preview, click the mask wrench icon
 and deselect preview from the drop-down list.
and deselect preview from the drop-down list.
Disable live preview
In addition, Premiere Pro has in-built features that optimize mask tracking:
For clips with a height greater than 1080, Premiere Pro scales the frame to 1080 before calculating the track. Also, Premiere Pro uses Low Quality renders to speed up the process of mask tracking.
Video tutorial
![]()
How to blur a moving face with masking and tracking
In this 5-min video tutorial, learn how to apply a feathered mask to protect a person's identity and then track that mask as it moves across the frame in a scene.
The tutorial provides you sample files to try out the feature for yourself.
Hiding Behind A Mask Drawing
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/premiere-pro/using/masking-tracking.html
Posted by: nicholsyall1945.blogspot.com








0 Response to "Hiding Behind A Mask Drawing"
Post a Comment